
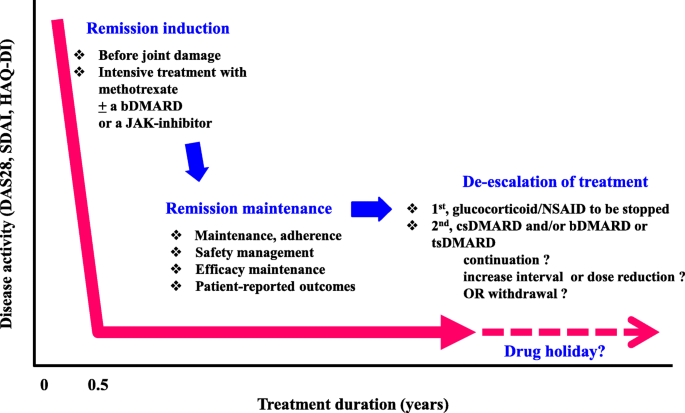
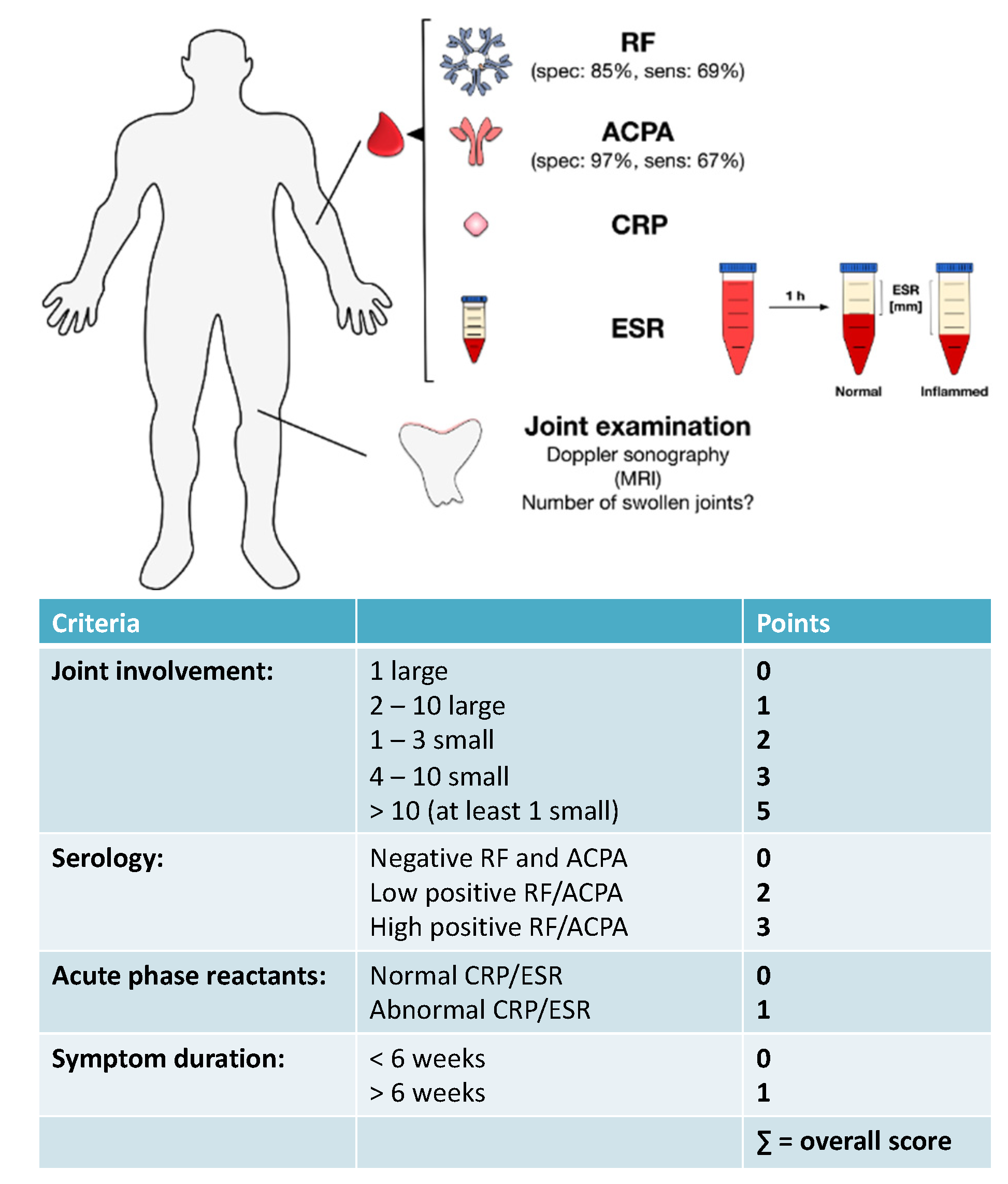
For example, CRP may be used to diagnose heart disease. Inflammatory markers such as erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP)īlood tests that measure body-wide inflammation can be used to diagnose other diseases, too.Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (called ACPA or anti-CCP).While no single blood test can be used to definitively diagnose rheumatoid arthritis, several blood tests can help measure inflammation that may be associated with the disease.īlood tests used to help diagnose or rule out rheumatoid arthritis include tests that detect: These symptoms cannot be explained by another condition, such as osteoarthritis or gout. Symptoms may include swelling, redness, warmth, pain, and stiffness, particularly after a long period of rest. People with rheumatoid arthritis usually experience joint symptoms that last 6 or more weeks. Points may be added over time or retrospectively, meaning the signs and symptoms do not necessarily have to be recorded at the same doctor’s appointment. Normal C-reactive protein (CRP) and normal erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) High positive results: Labs show elevated levels of ACPA or RF Low positive results: Labs show slightly elevated levels of ACPA or RF Negative results: Labs are negative for both anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (called ACPA, typically measured using an anti-CCP antibody test) and rheumatoid factor (RF) The person has experienced symptoms for 6 weeks or more The person has experienced symptoms for less than 6 weeks
More than 10 joints, including at least one small joint Joints Affectedġ large joint (for example, the knees, hips, shoulders, and elbows)ġ to 3 small joints (for example, knuckles of the hand or balls of the feet)Ĥ to 10 small joints (not including large joints) 2 A total point score of 6 or more indicates rheumatoid arthritis. These criteria (outlined below) set a minimum standard for what signs and symptoms must be noted before RA can be diagnosed. To help doctors make diagnoses, the American College of Rheumatology and the European League Against Rheumatism collaborated to create the 2010 Rheumatoid Arthritis Classification Criteria. While unproven, it is theorized that people with undifferentiated arthritis may be able to postpone or prevent RA from developing by taking steps to lower their risk (such as changing diet or stopping smoking).Ģ010 Rheumatoid Arthritis Classification Criteria

A person may have multiple appointments with a primary care physician and specialists before a diagnosis is made.
Diagnosing rheumatoid arthritis can be challenging, though. The sooner rheumatoid arthritis is accurately diagnosed, the sooner treatment can be started to limit its effects.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
